
Rules that try to protect pregnant female workers are more than confusing. There are conflicting and often overlapping laws and rules at the federal level. But worse, each state has its own rules and protections, or lack thereof. So if you are operating in multiple states keeping track of all this, and changes to state laws, is not a trivial task.
Worse yet, not complying with these laws is getting more expensive. The number of legal claims filed each year is increasing, and continues to increase. The U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) reported that claims increased 71% between 1992 and 2011.
However, The Department of Labor is here to save the day!
The DOL has created a comprehensive online tool that lists employee protections for pregnant or nursing women by state and territories like Puerto Rico, the U.S. Virgin Islands and Guam. Click the link to take a look.
DOL Pregnancy Discrimination Tool
The tool does a few things really well:
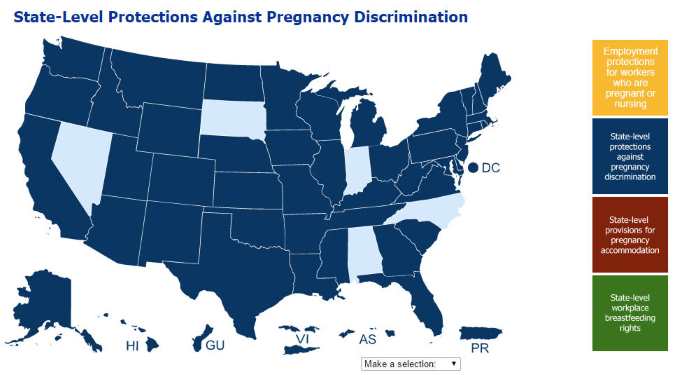
- You can click on color-coded policy boxes on the right to see which states support state-level workplace breastfeeding rights, protection against pregnancy discrimination, and pregnancy accommodation.
- You can select a state from a pick list and the web page will take you down to a detailed description of that pregnancy discrimination state's laws.
- Or, you can browse through the descriptions for each state and territory. Each section includes links to the authorizing state legislation on state web sites.
Is Pregnancy Discrimination a Thing?
So what is pregnancy discrimination? And is it a real thing?Federal Pregnancy Discrimination Act (PDA) of 1978
The federal Pregnancy Discrimination Act (PDA) of 1978, an amendment to Title VII, is a federal law banning pregnancy discrimination as a form of illegal discrimination on the basis of worker’s sex.
While it is not technically part of the American Disabilities Act, pregnancy became defined, by some, more as a temporary disability for a worker. Think of it like a physical handicap such as blindness, deafness or being wheelchair bound. To not take into account a pregnant worker’s new limitations caused by the pregnancy can be cause for a pregnancy discrimination lawsuit. Think this way if you are in California. If you are in Alabama, don’t think this way. 
Extreme Variation of Rules by State
Back to the tool. When you browse through The DOL tool you will notice a wide variation in protections by state.
California: Most Strict State
California is currently at the most protective state because it adds its own protections on top of federal laws.
First, the California Fair Employment and Housing Act does not allow any discrimination on the basis of sex. Pregnancy and childbirth breastfeeding are all covered by sex discrimination protections. So a woman that is pregnant, due to give birth, or is away from work due to childbirth or nursing can't be demoted, fired or have her pay modified in any way.
In fact, California rules allows pregnant women to take unpaid leave for up to four months of their pregnancy, child birth or other related medical conditions. California also protects pregnant women so they can be given less strenuous work during their pregnancy.
Less Strict States
At the other end of the spectrum are many states with less strict or no special rules.
Alabama doesn’t have laws to prevent pregnancy discrimination. In addition, Alabama also has no workplace breastfeeding rights. As it relates to pregnancy accommodation and pregnancy disability, there is sick time law for those situations, “State employees may use accrued sick time for maternity leave as long as they (1) work until actually disabled as a result of their pregnancy, and (2) return to work as soon as they cease to be disabled for that reason.” In other words, sick time must be used for the time that the worker must step out due to the pregnancy. Ala. Admin. Code § 670-X-14-.02.

Indiana has no state law covering Pregnancy Accommodation and Pregnancy-Related Disability, nor does it have one to protect against pregnancy discrimination. It does have a law supporting workplace breastfeeding rights.
North Carolina has no laws covering Pregnancy Accommodation and Pregnancy-Related Disability, pregnancy discrimination or workplace breastfeeding rights.
The Science Behind Protections
Research supporting these protections show that certain strenuous physical work can increase the rate of miscarriage and other complications for both the infant and mother’s health:
"A few studies, mostly performed in third world countries where occupational lifting during pregnancy is common, have found that heavy lifting is associated with increased risk of miscarriage in early pregnancy, increased pelvic pain, prematurity, low birth weight/ intrauterine growth restriction, mostly likely resulting from intermittent but prolonged reductions in blood flow to the uterus." (Source)
In short, without detailing all the differences, each state can likely have its own unique laws related to pregnancy, childbirth, nursing and family or medical leave that supplement or even override federal laws with higher-level protections for pregnant female workers. Or a state can have no state protections at all.
Here is an overview of the relevant laws included on the DOl interactive tool.
Federal Laws
- Title VII of the Civil Rights Act - 1964
This law made it illegal to discriminate against someone on the basis of race, color, religion, national origin or sex.
It cover employees who work for an employer having at least 15 employees. The law also applies to employment agencies, training programs and labor organizations, as well as to the federal government. - The Pregnancy Discrimination Act
This law covers women who are pregnant or have pregnancy-related conditions and says they can not be treated differently than other employees or job applicants.
- The Nursing Mothers Break Time Provision of The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (Affordable Care Act), 2010
Employers must provide reasonable break time for an employee to express breast milk for her nursing child for one year giving birth and for each time the employee has need to express the milk. Employers must include a place for this to take place and one that is shielded from view. Employers don't have to provide compensation during the time when milk is expressed
It goes without saying that you want to double check the state laws where you have business operations. Of course, you should always rely on your legal counsel when making any modifications to your internal human resource policies related to these issues.
You also want to make sure your systems can accommodate existing or changing rules over time. Pacific Timesheet time management systems can allow you to track any kinds of time off, breaks and capture important logs and notes about any accommodations that you might need to make for female workers covered by these rules.
Tell us what have been your biggest problems staying abreast of pregnancy discrimination rules? How do you monitor changes in these laws?
Image Credits: 1. dallascountyiowa.gov 2. okgov 3. ohio.gov



